Perte de cheveux et traitement

Aperçu
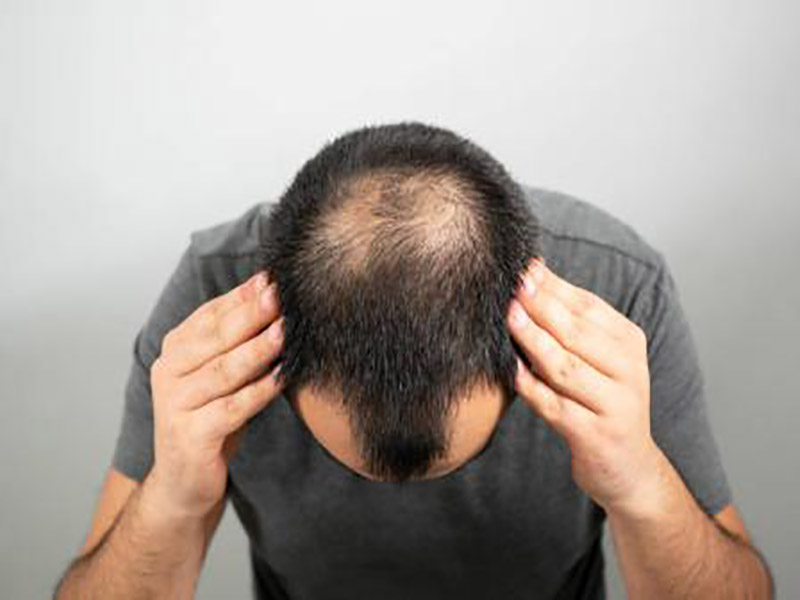
Le problème de l’alopécie a commencé à toucher de nombreuses personnes dans le monde. On la classe généralement en alopécie séborrhéique, alopécie neurogène, alopécie cicatricielle et alopécie pathologique, entre autres. Actuellement, le marché regorge de divers produits de repousse des cheveux, à la fois ingérables et topiques. Cependant, leur efficacité ultime reste incertaine, souvent en deçà de la capacité de fournir des résultats thérapeutiques définitifs. Les médicaments visent principalement à supprimer la sécrétion de dihydrotestostérone, mais leur efficacité est limitée et peut prédisposer les individus aux maladies cardiovasculaires et cérébrovasculaires. À l’inverse, la greffe de cheveux n’est pas universellement adaptée, compte tenu de son coût élevé et des risques chirurgicaux associés.
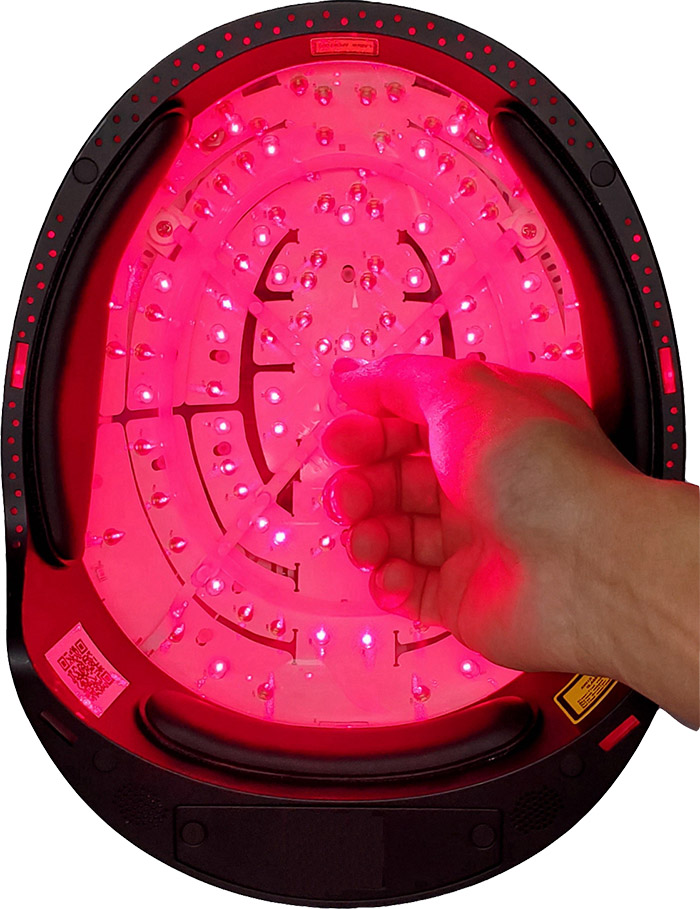
Actuellement, on trouve sur le marché des appareils de thérapie au laser de faible intensité (LLLT) utilisant la technologie laser doux avec une longueur d'onde de 650 à 670 nm. Ces appareils, communément appelés lasers doux, n'exercent aucun effet néfaste sur le corps humain et appartiennent au domaine de la physiothérapie. Ils promettent de traiter les problèmes de régénération des cheveux à la racine.
Une étude de marché sur l’approche des personnes souffrant de perte de cheveux face à cette pathologie répandue.
Le stress important, la prédisposition génétique, les réponses immunitaires anormales et le manque de sommeil sont apparus comme les principaux facteurs dans les réponses aux enquêtes sur l'alopécie. Parmi les causes de l'alopécie, le stress est devenu un facteur prédominant, tandis que la nature héréditaire de l'alopécie a également déclenché une augmentation significative des cas. Les problèmes immunitaires et le manque de sommeil ont également entraîné divers degrés de perte de cheveux. Bien qu'il y ait une sensibilisation accrue à l'alopécie, il existe une désinformation considérable concernant les soins et l'entretien des cheveux.
Environ 53 % des personnes souffrant de perte de cheveux ont essayé des méthodes préventives et de repousse au cours de l’année écoulée. Environ 60,3 % des personnes concernées utilisent des produits de soins capillaires à domicile, et seulement 3,5 % ont recours à des soins capillaires professionnels réguliers. De plus, 4,8 % recherchent un entretien capillaire intermittent dans des salons de coiffure, tandis que 31,4 % pensent qu’un lavage régulier est suffisant pour prendre soin de leurs cheveux.
Les principales modalités de traitement comprennent
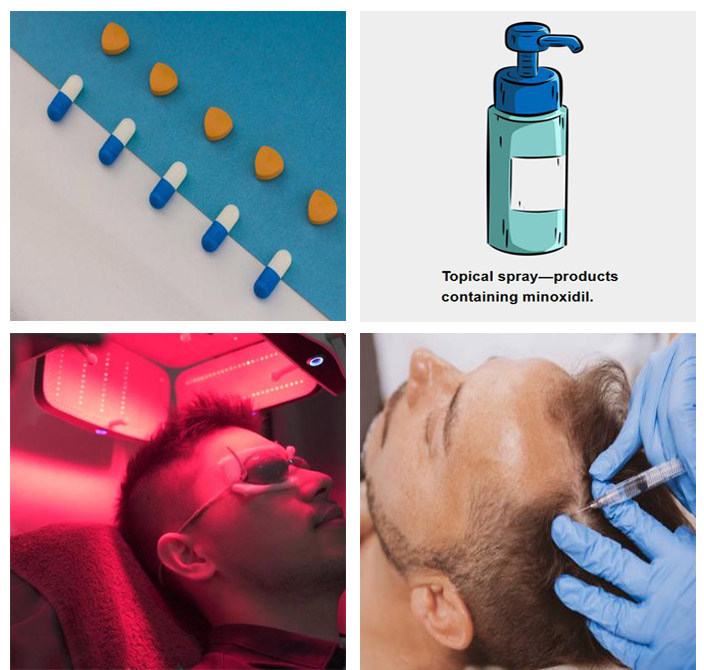
À l'échelle mondiale, il existe quatre méthodes éprouvées pour traiter efficacement la perte de cheveux : les médicaments par voie orale, les sprays topiques, la thérapie au laser de faible intensité et la thérapie par micro-aiguilletage. Examinons les avantages et les inconvénients de chaque méthode à des fins de comparaison.
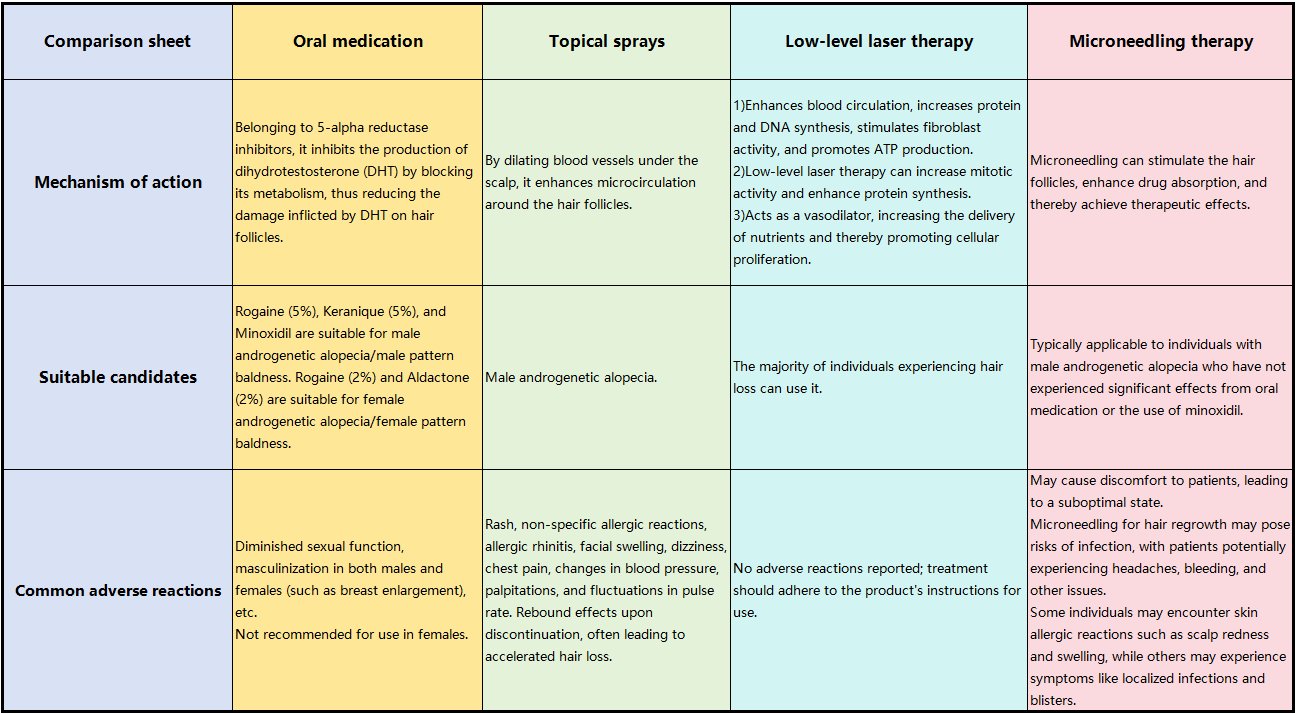
En résumé, la thérapie au laser de faible intensité est relativement sûre, largement applicable et donne les résultats les plus significatifs parmi les thérapies de repousse des cheveux.
Des recherches approfondies ont confirmé que la thérapie au laser à faible intensité (LLLT) peut modifier les propriétés oxydatives cellulaires, accélérer le transfert d'électrons, réguler l'expression génétique en contrôlant la fabrication et la réparation de l'ADN et induire la libération d'oxyde nitrique par les centres catalytiques cellulaires. Ces phénomènes entraînent une augmentation de la circulation sanguine, une synthèse améliorée des protéines et de l'ADN, une stimulation de l'activité des fibroblastes et la production d'ATP, entre autres effets. Grâce à de nombreuses années d'expérience clinique et de recherche, il a été démontré que la LLLT augmente l'activité mitotique et la synthèse des protéines, exerce des effets vasodilatateurs pour améliorer l'apport de nutriments, favorisant ainsi la prolifération cellulaire.
La LLLT utilisant une technologie laser douce de faible intensité peut faciliter les changements dans les follicules pileux.
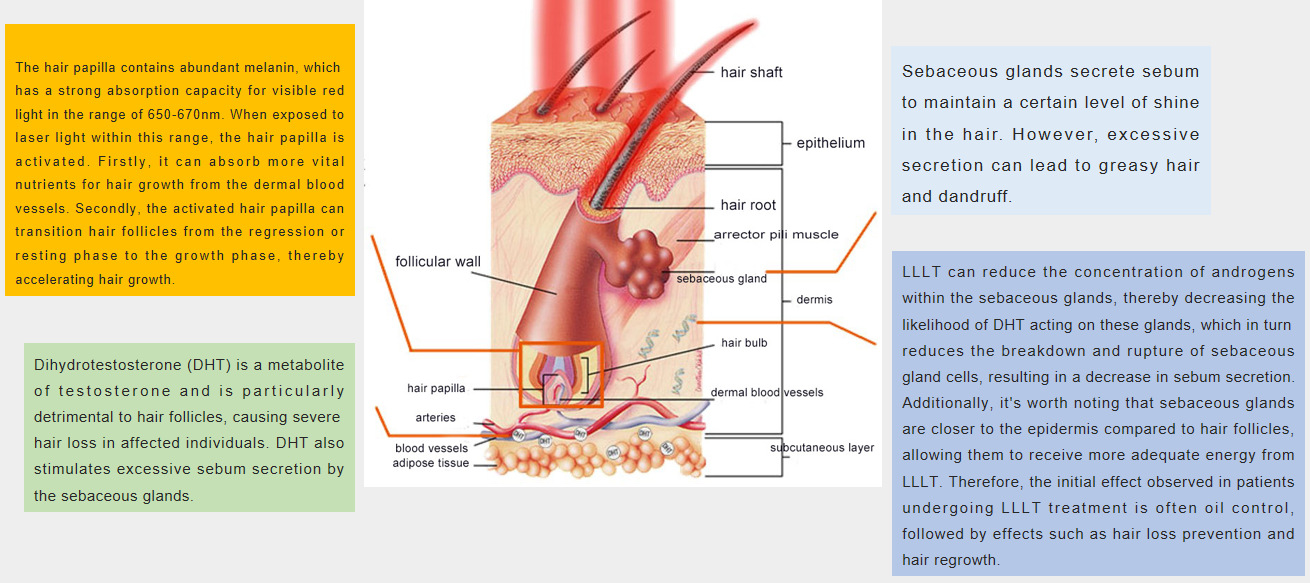
La papille pileuse à l’intérieur du follicule pileux contient une mélanine abondante, qui absorbe spécifiquement l’énergie du laser doux, formant ainsi la base physique de l’activation du follicule.
Après une irradiation laser douce, le tissu du cuir chevelu montre une augmentation de 54 % du flux sanguin du cuir chevelu et un apport en oxygène amélioré, indiquant un métabolisme accéléré.
Les activités enzymatiques associées à la croissance des cheveux, telles que la cytochrome oxydase et l'héparinase, augmentent. L'intensité de croissance du facteur de croissance nerveuse (NGF) est multipliée par cinq, facilitant la transition rapide des follicules pileux vers la phase de croissance.
Des études de biologie moléculaire ont également confirmé que le laser doux améliore l’expression génomique de nombreuses protéinases associées à la croissance des cheveux dans les tissus du cuir chevelu.
La LLLT utilisant la technologie laser doux de faible intensité ne peut pas modifier les séquences génétiques mais peut améliorer l'expression génomique spécifique liée à la croissance des cheveux, favorisant ainsi la repousse des cheveux.